Markets
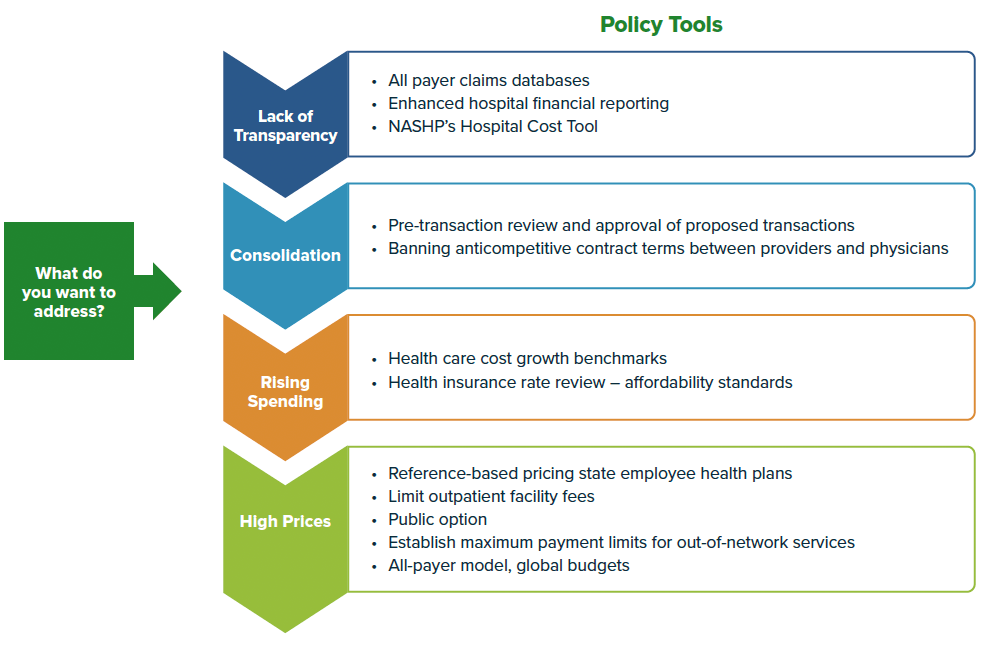
Policy Tools to Lower Hospital and Health System Costs
The post Policy Tools to Lower Hospital and Health System Costs appeared first on The National Academy for State Health Policy.
Policy Tools to Lower Hospital and Health System Costs
December 1, 2022
This toolkit is a resource for state policymakers interested in strategies to address high and rising hospital and health system costs. The toolkit includes resources to better understand the hospital cost data, model legislation and resources that the National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP) developed with guidance from states officials, as well as data and legal experts. For additional information, email Maureen Hensley-Quinn.

NASHP’s Hospital Cost Tool
To help state policymakers and their partners understand hospital costs from profits and losses on different payers to how much a hospital needs from commercial health plans to cover their expenses (also known as a hospital’s breakeven point), NASHP created the Hospital Cost Tool. Using annual hospital Medicare Cost Reports, the tool highlights a variety of different metrics for almost 5,000 hospitals.
See data below from NASHP’s Hospital Cost Tool – Median national hospital charges vs. operating costs

Resources:
- Hospital Cost Tool, which includes visual dashboards of multiple metrics, as well as a downloadable spreadsheet of all of the data within the website and more.
- NASHP Explainer: What is Breakeven?
- Q&A: What can states learn from the hospital cost tool?
Addressing Inappropriate Facility Fees on Certain Services
Facility fees are one of the key cost drivers resulting from consolidations. Physician practices purchased by health systems become outpatient departments of their parent hospital even if they are not located on the same campus. As a result, services at the acquired physician practices can be billed as a part of the overall health system that regularly charges facility fees. While they vary widely by health system, provider, and procedure, facility fees are increasingly added to bills for diagnostic testing and other routine services performed at physician’s offices. Restricting the addition of facility fee charges on services provided by outpatient physicians and diagnostic tests can help lower costs for consumers and disincentivize costly health system consolidation of independent providers.
Resources:
- Model State Legislation to Prohibit Unwarranted Facility Fees Reporting Requirements
- This model legislation prohibits site-specific facility fees for services rendered at physician practices and clinics located more than 250 yards from a hospital campus.
- It also prohibits all service-specific facility fees for typical outpatient services that are billed using evaluation and management codes, even if those services are provided on a hospital campus.
- Report: State Policies to Address Vertical Consolidation in Health Care
- Blog: Combat Rising Health Care Costs by Limiting Facility Fees with New NASHP Model Law
- Blog: Leveraging State Insurance Commissioners’ Authority to Lower Hospital Costs
Prohibiting Anti-Competitive Contract Clauses
Consolidation of hospitals and providers has created dominant health systems that can use their market power to include anticompetitive clauses in contracts with health plans, which help to drive up health care prices. Insurers may lack the leverage necessary to negotiate more flexible contract terms that could expand in-network providers, increasing competition and consumer choice that could lead to lower reimbursement rates. Prohibiting anticompetitive contract clauses allows insurers a better opportunity to navigate an already consolidated health market.
Resources:
- Model Act to Address Anticompetitive Terms in Health Insurance Contracts
- This model creates a more level playing field for negotiations to lower hospital costs by specifically prohibiting four common anticompetitive contract provisions that health systems have used in consolidated markets:
(1) all-or-nothing contracting;
(2) anti-tiering or anti-steering clauses;
(3) most-favored-nation clauses; and
(4) gag clauses.
Using Insurance Rate Review to Lower Hospital Costs and Incentivize Investments in Primary Care
The U. S. health care dollar is disproportionately spent on hospital services compared to primary care and behavioral health care. From 2015 to 2019, average hospital prices increased by 30%, a greater increase than any other category of medical care. Recognizing this challenge, Rhode Island uses its health insurance premium rate review authority to constrain commercial health plans’ reimbursement growth of hospital prices to the rate of inflation plus 1 percent while allowing greater price increases for primary and behavioral health services. Other states are moving to implement similar strategies that give the insurance commissioner the authority to enforce “affordability standards” as part of the health insurance rate review process.
Resources:
- Report: Toolkit for Assessing and Enacting Health Insurance Rate Review Authority to Control Health Care Costs – this toolkit allows states to assess their existing health insurance rate review laws for the authority to regulate hospital cost growth and proposes model statutory and regulatory text to condition health insurance rate approval on meeting affordability standards in hospital cost growth.
- Blog: Insurance Rate Review as a Hospital Cost Containment Tool: Rhode Island’s Experience
- Blog: Leveraging State Insurance Commissioners’ Authority to Lower Hospital Costs
- Policy Brief: Disrupting Hospital Price Increases: Using Growth Caps in Insurance Rate Review
Limiting Out-of-Network Provider Rates to Lower In-Network Prices and Increase Network Participation
Economic theory suggests that by setting a limit on out-of-network provider rates, hospitals and health systems will be incentivized to negotiate with health plans increasing the likelihood of lower in-network reimbursements. Out-of-network rate limits can be established by using a multiple of Medicare’s rate or leveraging the in-network rate. Ultimately, this policy aims to reduce the value of the hospital threat to stay out-of-network and reduce overall spending.
Resources:
- Model State Legislation: An Act to Limit Out-of-Network Provider Rates
- This model legislation limits out-of-network rates for inpatient and outpatient hospital services to the lesser of (a) the state’s median in-network commercial rate for the same service; or (b) a percentage of the Medicare rate for the same service in the same geographic area.
- Q&A: Model State Legislation to Limit Out-of-Network Provider Rates
Implement Price Ceilings for All Providers, Including Hospitals Using Reference-Based Pricing
Reference-based pricing (RBP) lowers hospital prices by using Medicare’s cost-based reimbursement rates as a reference point for how much private insurers pay hospitals. Private insurers negotiate prices as a discount off a hospital’s charges, but charges at hospitals in the U.S. are much higher than costs and have risen dramatically since 2011. RBP can better ensure prices are based on a hospital’s costs, not its charges, offering predictability and lower prices.
Resources:
- NASHP’s Cost-Containment Toolkit offers resources related to RBP, including an overview chart showing tens of millions in savings for states engaged in this strategy.
The post Policy Tools to Lower Hospital and Health System Costs appeared first on The National Academy for State Health Policy.

Wittiest stocks:: Avalo Therapeutics Inc (NASDAQ:AVTX 0.00%), Nokia Corp ADR (NYSE:NOK 0.90%)
There are two main reasons why moving averages are useful in forex trading: moving averages help traders define trend recognize changes in trend. Now well…
Spellbinding stocks: LumiraDx Limited (NASDAQ:LMDX 4.62%), Transocean Ltd (NYSE:RIG -2.67%)
There are two main reasons why moving averages are useful in forex trading: moving averages help traders define trend recognize changes in trend. Now well…
Seducing stocks: Canoo Inc (NASDAQ:GOEV 5.43%), Ginkgo Bioworks Holdings Inc (NYSE:DNA -1.12%)
There are two main reasons why moving averages are useful in forex trading: moving averages help traders define trend recognize changes in trend. Now well…